Imagine you want to prove to a friend that you know the secret password to a clubhouse, but you don't want to actually tell them the password. How could you do it?
This is the core idea behind a Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP), a cryptographic method that allows one person (the Prover) to prove to another (the Verifier) that a certain statement is true, without revealing any information other than the fact that the statement is true.
For this cryptographic magic to work, any ZKP system must guarantee three properties:
- Completeness: If your statement is true and you are honest, you will always be able to convince the Verifier.
- Soundness: If your statement is false, you cannot trick the Verifier into believing it's true (except with a vanishingly small probability).
- Zero-Knowledge: The Verifier learns absolutely nothing about your secret information, other than the fact that your statement is true.
How Do We Prove Something Without Revealing It?
The process translates a real-world statement into a mathematical problem that a computer can verify. It can be broken down into a logical flow:
Step 1: Translate Your Claim into a "Circuit"
First, we need to define exactly what we want to prove. This is done by creating what developers call an arithmetic circuit. Think of a circuit not as a physical object with wires, but as a precise set of rules or a logical flowchart for a specific claim.
For example, if you want to prove you are over 18 without revealing your birthday, the circuit would be designed to perform a single check: "Is the date of birth provided earlier than this date 18 years ago?"
Step 2: Make the Rules Transparent
This step is crucial for building trust. The logic of the circuit is made public (open-sourced) so that anyone can inspect the "rules of the game."
This ensures that the circuit is fair, unbiased, and doesn't leak any private information.
Step 3: Generate and Verify the Proof
Once the rules are trusted, the Prover takes their secret information (their actual date of birth) and runs it through the circuit on their own device.
The circuit generates a small, cryptographic file, the proof.
The Prover then sends this proof to the Verifier, who performs a quick mathematical check. If it passes, they are cryptographically certain that the Prover's claim is true, without ever seeing the secret data.
From Theory to Practice: Which ZKP Does zkMe Use?
Now that we understand the fundamental concept of Zero-Knowledge Proofs, a natural question arises: How is this actually implemented in the real world?
The three-step process we described is a high-level overview, but the specific cryptographic techniques used to make it work can vary significantly.
Over the years, researchers have developed several different ZKP systems, each with its own trade-offs in terms of proof size, verification speed, and setup requirements. Some of the most well-known include zk-SNARKs, zk-STARKs, and Bulletproofs.
So, which one does zkMe use for its zkKYC solution? The answer is zk-SNARKs, specifically an implementation called Groth16. Let's take a closer look at what makes zk-SNARKs special and why it's a powerful choice for identity verification.

What is zkKYC - The Private and Compliant Digital Identity
A Deeper Dive: What is a zk-SNARK?
zk-SNARK stands for Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge. Let's break down what each part of this acronym means, as it reveals why zk-SNARKs are so revolutionary, particularly for applications like blockchain and digital identity.
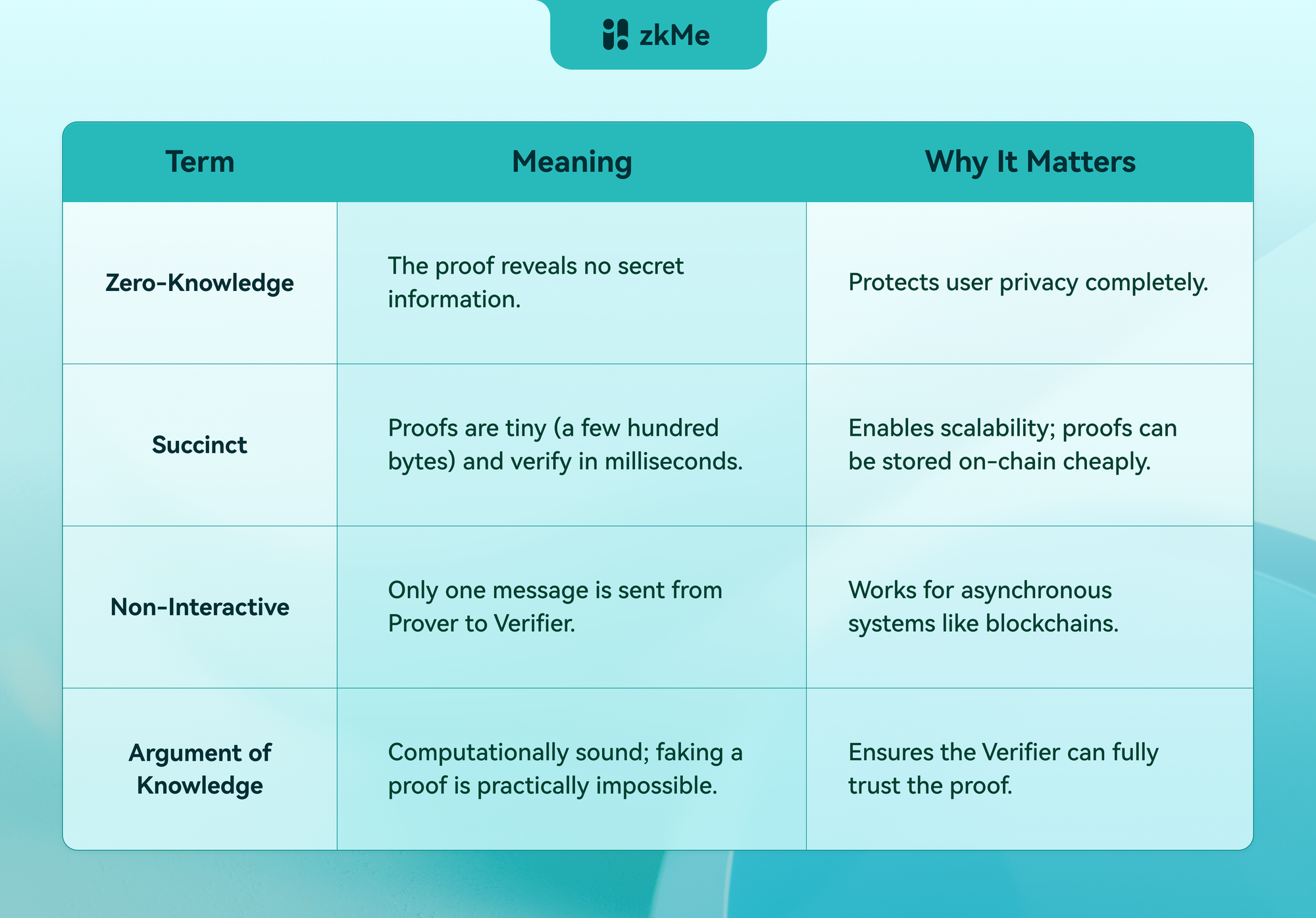
The Magic Ingredient: Polynomials
So, how can a zk-SNARK verify a potentially massive computation so efficiently? The secret lies in converting the computational problem into a question about polynomials. As Vitalik Buterin explains, a single equation between polynomials can represent an unbounded number of equations between numbers.
Instead of checking every step of a computation (which would be slow), a zk-SNARK converts the entire computation into a complex polynomial. The Prover then creates a proof that they know a polynomial that satisfies certain properties. The Verifier can check this proof with a single equation, instantly verifying the entire original computation without having to re-run it. This clever mathematical trick is what makes zk-SNARKs both "succinct" and powerful.
The "Trusted Setup"
A key characteristic of many zk-SNARKs (like Groth16, which is used by zkMe) is the need for a Trusted Setup. This is a one-time ceremony performed when a new circuit is created to generate a special key (a common reference string) needed for proving and verifying. This process creates a secret (the "toxic waste") that must be destroyed. To ensure security, this is done through a multi-party ceremony where as long as at least one participant is honest and destroys their part of the secret, the system is secure.
Conclusion: Trustworthy Verification for a Private World
Zero-Knowledge Proofs, and zk-SNARKs in particular, represent a monumental leap forward in cryptography. They solve the fundamental conflict between verification and privacy. By allowing us to prove facts without revealing the underlying data, they provide the foundation for a new generation of technology: from scalable and private blockchains to secure digital identity systems like zkKYC, that are both trustworthy and respectful of our fundamental right to privacy.
Ready to unlock the power of Zero-knowledge Proof?
About zkMe

zkMe provides protocols and oracle infrastructure for the compliant, self-sovereign, and private verification of Identity and Asset Credentials.
It is the only decentralized solution capable of performing FATF-compliant CIP, KYC, KYB, and AML checks natively onchain, without compromising the decentralization and privacy ethos of Web3.
By combining zero-knowledge proofs with advanced encryption and cross-chain interoperability, zkMe enables verifiable identity and compliance data to remain entirely under the user's control. This ensures that sensitive information never leaves the user's device while maintaining regulatory-grade assurance for partners and protocols.







